Architecture
Architecture summary of FRSCA.
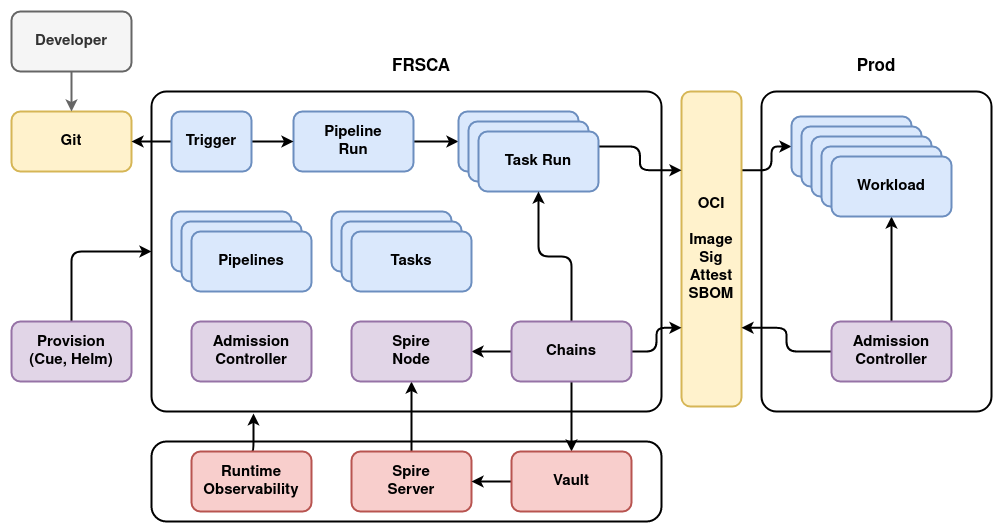
Diagram of Key Components
Provisioning
The environment is provisioned using make setup-frsca which deploys a variety
of Cue definitions and Helm charts. The resulting environment contains Tekton,
Chains, Spire, Vault, the various Tasks, and Pipeline definitions.
When the infrastructure starts, several components will be defined or running:
- Pipelines, Tasks, and Triggers will be defined according to the definition of the environment.
- Cert-manager is deployed in the FRSCA setup to allow the various components running inside the cluster to use TLS. In many environments, components like Vault, Spire, and the OCI Registry would be external to the cluster and have a certificate signed by a public authority or the company's internal CA.
- Vault is deployed with development settings inside the cluster. In many environments, this would be managed outside of the cluster.
- Spire is deployed inside the cluster. This is also typically deployed and managed external to the cluster.
- Vault is configured with the transit plugin and a long term signing key to sign images. Authorization is configured to require a valid OIDC credential from Spire. The public signing key is exported from the transit plugin and loaded into tooling that needs to verify image signatures.
- Chains is configured to perform signing with Vault and request a Spire credential from the Spire Node.
- The Spire Node provides credentials to Chains after verifying the Kubernetes service account and namespace of Chains.
- An admission controller is configured to require all containers deployed in the FRSCA cluster have been signed by the team that provisions the cluster.
Pipeline
The following actions occur in a typical pipeline:
- A developer commits their code to a Git server. That server will typically require multiple reviewers to permit a merge into the main branch.
- A Tekton trigger detects the change and creates a PipelineRun.
- The PipelineRun runs one or more TaskRun steps, each of which are monitored by Chains.
- TaskRun steps will include SBOM generation and vulnerability scanning.
- A TaskRun step pushes the image and associated SBOM to an OCI repository.
- Chains creates an attestation of the steps performed in the task run.
- Chains signs the image and attestation using credentials from Spire and Vault for the signing.
- Chains pushes attestations and signatures to the OCI repository.
Production Recommendations
- Production should be hardened per recommendations from CIS and similar organizations.
- The admission controller in production should prevent containers from being deployed with privileged access to the host for all user workloads.
- The admission controller should also be configured with the public signing key exported from Vault, and require images to be signed with that key.